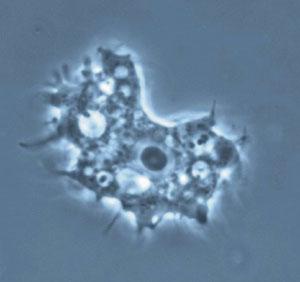
Acanthamoeba is a genus of amoebae, one of the most common protozoa in soil, and also frequently found in fresh water and other habitats. The cells are small, usually 15 to 35 μm in length and oval to triangular in shape when moving. The pseudopods form a clear hemispherical lobe at the anterior, and there are various short filose extensions from the margins of the body. These give it a spiny appearance, which is what the name Acanthamoeba refers to. Cysts are common. However, these amoeba can also act as opportunistic as well as nonopportunistic pathogens. They are the causative agents of granulomatous amoebic encephalitis and amoebic keratitis and have been associated with cutaneous lesions and sinusitis. Immuno compromised individuals, including AIDS patients, are particularly susceptible to infections with Acanthamoeba.
The trophozoite is irregular, 15-45 μm, having micropseudopodia called acanthopodia. In trichrome stain the cytoplasm of trophozoites appears greenish pink. The central located kariosome pink or red. The cysts are spherical, 15-20 μm in diameter, having a thick double wall. The outer wall may be spherical or wrinkled, the inner wall appear stellate or polyhedral. Both forms have a single nucleus with a large centrally located nucleolus. With trichrome stain, the cysts stain red. Species identification is based on morphology of cysts (stellate, polyhedral).