CHEMICAL SUBSTANCE DATASHEET
|
CHEMICAL SUBSTANCE IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
Chemical name |
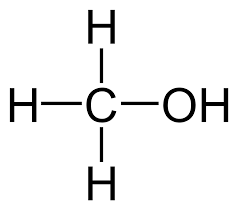
Methanol [1] |
|
Synonyms |
|
|
IUPAC name |
|
|
CAS No |
67-56-1 |
|
REACH registration number |
|
|
EC No |
200-659-6 |
|
Molecular formula |
CH4O |
|
Substance group/chemical family |
Mono constituent substance/Organic/Alcohol (100%) |
|
Appearance Physical state Odour Form Colour |
Liquid (100%) @ 20°C and 1013 hPa Slight alcoholic odour when pure; repulsive, pungent odor when crude [3]
colourless [3] |
|
USES AND HANDLING ISSUES |
|
|
Relevant identified uses |
Methanol is an important commercial chemical. It is used as a solvent, fuel additive, antifreeze, in home heating oil and to make many different chemicals. Methanol is an ingredient in many products for car and home maintenance and arts and crafts. [3] |
|
Handling considerations |
Prevention statementsWhen handling this substance: do not breathe the dust, fume, gas, mist, vapours or spray; keep away from heat, sparks, open flames and/or hot surfaces – No smoking; use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area; keep container tightly closed; use personal protective equipment as required.; wear protective gloves and/or clothing, and eye and/or face protection as specified by manufacturer/supplier. Response statementsIn case of incident: If exposed or you feel unwell: call a poison center or doctor/physician. If on skin (or hair): take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with water or shower. Storage statementsStore this substance locked up. [1] |
|
PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
Molecular weight |
|
|
Bulk density/Specific gravity |
relative density : 0.79 at 20°C [1] |
|
pH |
|
|
Particle size |
|
|
EC |
|
|
Melting/Freezing point |
-97.8 °C at 101 325 Pa [1] |
|
Boiling point |
64.7 °C at 101 325 Pa [1] |
|
Flash point |
9.7 °C at 101 325 Pa [1] |
|
Flammability |
Flammable (100%) [1] |
|
Vapour density |
(air = 1): 1.1 [3] |
|
Vapour pressure |
16.927 kPa @ 25 °C [1] |
|
Solubility in water |
1 000 g/L @ 20 °C [1] Substance is completly miscible in water at 20°C. [2] |
|
Solubility in organic solvents |
Miscible with ethanol, ether, benzene, most organic solvents and ketones [3] |
|
Solubility in inorganic solvents |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
|
|
Ionicity in water |
|
|
Surface tension |
Based on chemical structure, no surface activity is predicted. [2] |
|
Dispersion properties |
|
|
Explosiveness |
non-explosive (100%) [1] |
|
Other properties |
autoflammability / self-ignition: 455 °C at 101 325 Pa [1] dynamic viscosity: 0.544 - 0.59 mPa s [1] |
|
Stability and reactivity |
|
|
Chemical stability |
|
|
Reactivity hazards |
Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions: Carbon oxides [3] |
|
Corrosivity |
|
|
Polimerization |
|
|
Incompatibility with various substances |
Acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents, alkali metals, reducing agents, acids. [3] There is an/ explosive nature of mixtures of aluminum or magnesium with methanol. [3] |
|
Special remarks on reactivity |
Non oxidising (100%) [1] The substance is incapable of reacting exothermically with combustible materials on the basis of the chemical structure. [2] |
|
Physical, chemical and biological coefficient |
|
|
Koc |
0.13-1.00 [2] |
|
Kow |
-0.77 @ 20 °C [2] |
|
pKa |
15.3 [3] |
| log Koa | 2.88 (Octanol-Air partition coefficient) [3] |
|
log Kp |
|
|
Henry-constant |
0.461 Pa.m³.mol-1 @ 20 °C [1] |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE AND BEHAVIOUR |
|
|
Artificial pollution sources |
Methanol's production and use as a solvent, fuel additive, and in the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid, and methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Its use in hydraulic fracturing fluids will result in its direct release to the environment. It can also be released directly to the environment in exhaust gases from combustion engines. Methanol has been identified as a natural emission product from various plants and as a biological decomposition product of biological wastes and sewage; natural emission sources include volcanic gases, vegetation, microbes, and insects, and methanol is a product of decaying organic material. [3] |
|
General terrestrial fate |
If released to soil, methanol is expected to have very high mobility based upon a measured Koc of 2.75. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 4.55X10-6 atm-cu m/mole. Methanol may also volatilize from dry soils based upon its vapor pressure. Biodegradation half-lives of 1 and 3.2 days measured in a sandy silt loam and sandy loam from Texas and Mississippi, respectively, suggest that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process in soil. [3] Methanol is readily biodegradable in water, soil and sediments, both under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. [2] |
|
General aquatic fate |
If released into water, methanol is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. Estimated volatilization half-lives for a model river and model lake are 4.6 and 35 days, respectively. Rapid biodegradation in a variety of screening studies using sewage seed and activated sludge inoculum suggests that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process in water. BCF values of less than 10 in fish suggest that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis and photolysis are not expected to be an important environmental fate processes since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze and photolyze under environmental conditions. [3] Methanol is readily biodegradable in water, soil and sediments, both under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. [2] |
|
General atmospheric fate |
According to a model of gas/particle partitioning of semivolatile organic compounds in the atmosphere, methanol, which has a vapor pressure of 127 mm Hg at 25 °C, is expected to exist solely as a vapor in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase methanol is degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 17 days, calculated from its rate constant of 9.0X10-13 cu cm/molecule-sec at 25 °C. The major degradation product from reaction with hydroxyl radicals is formaldehyde. [3] Methanol is degraded in the atmosphere by photochemical, hydroxyl-radical dependent reactions. [2] Half life in air (DT50): 17 days [1] |
|
General persistence and degradability |
|
|
Abiotic degradation and metabolites |
|
|
Biodegradation and metabolites |
Readily biodegradable (100%) [1] Biodegradation: 71.5 – 95 % (freshwater, wastewater), 69 - 97 % (marine water) [2] 53.4 % (soil, aerobic conditions) and 46.3 % (anaerobic conditions) after 5 days [2] |
|
Bioconcentration |
No bioaccumulation potential [1] Given the value of the Henry's Law constant, once in water, methanol is likely to remain in the aqueous phase.No bioaccumulation is expected. [2] Methanol does not significantly bioaccumulate in fish. Experimental BCFs of < 10 in fish species, including Cyprinus carpio and Leuciscus idus, have been reported. [2] |
|
Volatilization |
The Henry’s Law constant indicates that volatilization is not a significant removal process from the aquatic compartment. [2] |
|
Photolysis |
Methanol is degraded in the atmosphere by photochemical, hydroxyl-radical dependent reactions. [2] |
|
Hydrolysis |
With respect to the aquatic environment methanol, as an alcohol, lacks hydrolysable groups and is chemically stable in water. [2] |
|
Soil adsorption and mobility |
Due to the high solubility of methanol in water and its low octanol-water partition coefficient adsorption to soil is considered to be negligible. [2] Adsorption on soil is not to be expected due to the high solubility of methanol as well as its low octanol-water partition coefficient. The adsorption of methanol onto three different soil types at 6 deg C was studied. Adsorption coefficients of between 0.13 and 0.61 were measured for all soil types and at all concentrations. A Koc of 1 was calculated . These coefficients indicate that methanol has a low adsorptive capacity on soils. [2] |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL CONCENTRATIONS |
|
|
Measured data |
Methanol has been identified as a volatile emission product from evergreen cypress trees. Methanol is formed during biological decomposition of biological wastes, sewage, sludges and various organic compounds. Natural emission sources include volcanic gases, vegetation, microbes, and insects. Methanol is a product of decaying organic material. [3] Distribution in media: air: 12.5 - 73.3 % water: 15.6 - 87.5 % soil: 0 - 11.1 % sediment: 0 - 0.02 % suspended sediment: 0% biota: 0% aerosol 0% [1] |
|
ECOTOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION |
|
|
General adverse effects on ecosystem |
|
|
Acute toxicity (LC50, EC50) |
|
|
Aquatic systems |
LC50: 15.4 g/L (freshwater fish, 4 days) [1] EC50 : 22 g/L (freshwater algae, 4 days) [1] EC50: 20 g/L (microorganisms) [1] |
|
Terrestrial systems |
|
|
Chronic toxicity (NOEC, LOEC) |
|
|
Aquatic systems |
EC10 / LC10 or NOEC: 450 mg/L (freshwater fish) [1] EC10 / LC10 or NOEC: 208 mg/L (freshwater invertebrates) [1] |
|
Terrestrial systems |
Long-term EC10 / LC10 / NOEC: 10 g/kg soil dw (terrestrial macroorganisms except arthropods) EC10 / LC10 / NOEC: 1.555 g/kg soil dw (terrestrial plants) [1] |
|
HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS and PROTECTION |
|
|
Routes of human exposures |
inhalation, oral, dermal |
|
General effects |
irritation eyes, skin, upper respiratory system; headache, drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting; visual disturbance, optic nerve damage (blindness); dermatitis [3] |
|
Endocrine disruption |
|
|
Mutagenicity |
Based on the negative results in the in vivo studies, methanol does not appear to be mutagenic. As a result the substance is not considered to be classified for genetic toxicity under Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008, as amended for the tenth time in Regulation (EU) No 2017/776. [2] |
|
Carcinogenicity |
No adverse effect observed (chronic, inhalation route, mouse) [1] In mouse and rat effects were shown, but can not be transfered to humans. As a result the substance is not considered to be classified for carcinogenicity under Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008, as amended for the tenth time in Regulation (EU) No 2017/776. [2] |
|
Reprotoxicity |
Fertility: No adverse effect observed (subchronic, oral route, mouse; chronic inhalation route, rat) [1] Based on major species differences between humans and rodents (metabolic pathway/enzymes, mode of action, toxicokinetics), considering the overall weight of evidence, and in line with the evaluation of reproductive toxicity provided by the Committee for Risk Assessment (RAC, 2014), methanol does not appear to be toxic to reproduction. As a result the substance is not considered to be classified for toxicity to reproduction under Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008, as amended for the tenth time in Regulation (EU) No 2017/776. [2] |
|
Teratogenicity |
Developmental toxicity: Adverse effect observed (subchronic, oral route, mouse; subacute, inhalation route, rat) |
|
Skin, eye and respiratory irritations |
Skin: No adverse effect observed (not irritating) [1] Eye: No adverse effect observed (not irritating) [1] Respiratory: No study available [1] |
|
Metabolism: absorption, distribution & excretion |
Adsorption: Oral: 100 %, Inhalation: 60 % [1] No bioaccumulation potential [1]
|
|
Exposure limits |
DNEL: 130 mg/m³ (systemic and local effects, workers, long term & acute short term, inhalation, acute toxicity) DNEL: 20 mg/kg bw/day (systemic, workers, long term& acute short term, dermal, acute toxicity) DNEL: 26 mg/m³ (systemic and local effects, general population, long term & acute short term, inhalation, acute toxicity) DNEL: 4 mg/kg bw/day (systemic, general population, long term& acute short term, dermal, acute toxicity) DNEL: 4 mg/kg bw/day (systemic, general population, long term& acute short term, oral, acute toxicity) [1] |
|
Drinking water MAC |
|
|
Other information |
Skin sensitisation: No adverse effect observed (not sensitising) [1] Respiratory sensitisation: No study available [1] Genetic Toxicity – InVitro: Adverse effect observed (positive) [1] Genetic Toxicity – InVivo: No adverse effect observed (negative) [1] |
|
Animal toxicity data |
|
|
Acute toxicity (LD50) |
LD50: 1 187 mg/kg bw (oral route) Adverse effect observed [1] LC50: 43 700 mg/m³ (inhalation route) Adverse effect observed [1] LD50: 17 100 mg/kg bw (dermal route) Adverse effect observed [1] |
|
Chronic toxicity (NOEL, LOEL) |
LOAEL: 2 340 mg/kg bw/day (subacute, monkey, oral route - systemic effects, repeated dose toxicity)- Adverse effect observed [1] NOAEC 13 mg/m³ (chronic, monkey, Inhalation route - systemic effects, repeated dose toxicity) - No adverse effect observed [1] NOAEC 1 300 mg/m³ (chronic, mouse, carcinogenicity, inhalation route) [1] NOAEL: 1 000 mg/kg bw/day (subchronic, mouse, reprotoxicity, fertility, oral route) No adverse effect observed [1] NOAEC 1 300 mg/m³ (chronic, rat, reprotoxicity, fertility, inhalation route) No adverse effect observed [1] LOAEL 1 700 mg/kg bw/day (subchronic, mouse, reprotoxicity, developmental toxicity, oral route), Adverse effect observed [1] NOAEC 1 330 mg/m³ (subacute, rat, reprotoxicity, developmental toxicity, inhalation route), Adverse effect observed [1] |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS |
|
| REACH/CLP |
Danger! According to the harmonised classification and labelling (CLP00) approved by the European Union, this substance is toxic if swallowed, is toxic in contact with skin, is toxic if inhaled, causes damage to organs and is a highly flammable liquid and vapour. Additionally, the classification provided by companies to ECHA in REACH registrations identifies that this substance is suspected of causing cancer. [1]
According to REACH registrations: H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapour. H331: Toxic if inhaled. H370: Causes damage to organs. H301: Toxic if swallowed. H311: Toxic in contact with skin.
According to CLP notifications: H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapour. H331: Toxic if inhaled. H370: Causes damage to organs. H301: Toxic if swallowed. H311: Toxic in contact with skin.
Properties of concern: There is no overall agreement among data submitters, but a minority indicate they consider this substance as Persistent, Bioaccumulative and Toxic (0.37% of REACH registrations). [1] |
|
EINECS regulation |
̵ |
|
OSHA regulations etc. |
|
|
OTHER INFORMATION, SPECIAL REMARKS |
|
|
Classification and proposed labelling with regard to toxicological data |
|
|
|
|
|
CREATED, LAST UPDATE |
|
|
Created |
2019. 12. 02 |
|
Last update |
2020. 06. 01 |
|
REFERENCES |
|
|
[1] ECHA, https://echa.europa.eu/hu/brief-profile/-/briefprofile/100.000.599, Accessed 2019.11. 29 [2] ECHA, Methanol, https://echa.europa.eu/hu/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/15569/4/8, Accessed 2020.06. 01 [3]PUBCHEM, Methanol, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Methanol, Accessed 2020.06. 01 |
|