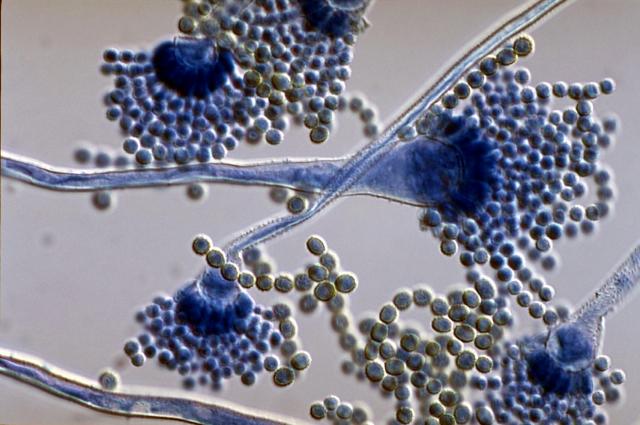
Microscopical view of conidia of Aspergillus flavus mold, with the budding conidiospores and the releasing conidia.
Aspergillus flavus is the second most common patogen of aspergillosis after Aspergillus fumigatus. A. flavus invades blood vessels in human lung or brain and cause infarction. Patients infected with A. flavus often have reduced or compromised immune systems.
Classification of A. flavus:
- Kingdom: Fungi
- Phylum: Ascomycota
- Class: Eurotiomycetes
- Order: Eurotiales
- Family: Trichocomaceae
- Genus: Aspergillus
Aspergillus flavus produces a toxin called aflatoxin, a very toxic substance, which occur in infected grain.
Aflatoxins are toxic and carcinogenic chemical substances, hazardous for plant, animal and human organims. The fungus A. flavus can infect seeds of corn, peanuts, cotton, and nut trees.You can often see the sporulating mould on the injured kernels of maize or other grain species.
A. flavus lives in soil and plays important role in the element cycling by using dead organic material as nutrient.
Unlike most fungi, Aspergillus flavus is favored by hot dry conditions. The optimum temperature for growth is 37 oC (98.6 F), but the fungus readily grows between the temperatures of 25–42 oC (77–108 F), and will grow at temperatures from 12–48 oC (54–118 F). Such a high temperature optimum contributes to its pathogenicity on humans.
Click on this link to see more pictures on microorganisms!
Scheidegger, K. A. and G. A. Payne. 2003. Unlocking the secrets behind secondary metabolism: A review of Aspergillus flavus from pathogenicity to functional genomics. Journal of Toxicology-Toxin Reviews. 22(2-3): 423-459.
http://www.aspergillusflavus.org/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspergillus_flavus