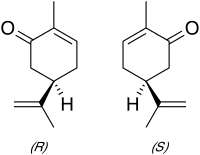
Carvone is a member of a family of chemicals called terpenoids.Carvone is found naturally in many essential oils, but is most abundant in the oils from seeds of caraway (Carum carvi) and dill. It is used as mosquito repellents as well as flavourings.
Identifiers
- CAS number 99-49-0 (racemic) Yes, 2244-16-8 ((S)-Carvone)
- ChemSpider 21106424 (racemic) Yes, 15855 (S-(+) enantiomer), 388655 (R-(-) enantiomer)
- UNII 75GK9XIA8I
- KEGG C01767
- ChEBI CHEBI:38265
- ChEMBL CHEMBL15676
- RTECS number OS8650000 (R) OS8670000 (S)
Properties
- Molecular formula C10H14O
- Molar mass 150.22 g/mol
- Appearance Clear, colorless liquid
- Density 0.96 g/cm3
- Melting point 25.2 °C
- Boiling point 231 °C, 91 °C (@ 5 mmHg)
- Solubility in water Insoluble (cold)
- Slightly soluble (hot)/soluble in trace amounts
- Chiral rotation [α]D −61° (R)-Carvone 61°(S)-Carvone
Hazards
- R-phrases R22
- S-phrases S36
- Main hazards inflammable
Environmental Fate/Exposure Summary
Carvone's production and use as a flavoring liqueur, in perfumery and soaps, and as a carminative may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Carvone is found naturally in caraway and dill seed oils, mandarin seed oil, spearmint oil, and gingergrass oil. If released to soil, carvone will have high mobility in soil. Volatilization of carvone may be important from moist and dry soil surfaces. Insufficient data are available to determine the rate or importance of biodegradation of carvone in soil. If released to water, carvone will not adsorb to suspended solids and sediment in the water. Carvone may volatilize from water surfaces with estimated half-lives for a model river and model lake of 17.5 hours and 9 days, respectively. An estimated BCF value of 11 suggests that carvone will not bioconcentrate in aquatic organisms. Insufficient data are available to determine the rate or importance of biodegradation of carvone in water. If released to the atmosphere, carvone will exist in the vapor phase in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase carvone is degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be about 2.7 hours. Vapor-phase carvone may also react with ozone, the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be about 3.2 hours. Particulate-phase carvone may be physically removed from the air by wet and dry deposition. The general population can be exposed to carvone through various foodstuffs. (SRC)
In the EU it has been evaluated and recommended for classification and labeling as a sensitizer, in 2013.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carvone
http://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/06316e80-54ad-455b-9ef2-5774d45aaf99
http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=439570#x351